Personal Insurance: Types, Coverage & How to Choose
Personal insurance protects you and your family from everyday financial risks—like medical bills, accidents, property damage, theft, legal claims, and unexpected emergencies. The goal isn’t to “buy everything.” The goal is to choose the right protection for your lifestyle, responsibilities, and budget.
Insurance rules and policy terms can vary by country and provider, but the core idea is the same everywhere: you pay a premium to transfer certain risks to an insurer—so one bad day doesn’t become a long-term financial crisis.
What personal insurance can cover (and what it usually doesn’t)
Depending on the policy, personal insurance may help cover:
- Hospital and medical expenses (health insurance)
- Financial support for your family if you pass away (life insurance)
- Damage to your vehicle and liability to others (auto insurance)
- Theft, fire, and damage to your home or belongings (home/renters insurance)
- Legal liability if you accidentally injure someone or damage their property (personal liability coverage)
- Trip cancellations, medical emergencies abroad, baggage loss (travel insurance)
Common exclusions often include:
- Intentional damage or fraud
- Normal wear and tear (especially for property)
- Pre-existing conditions (some health/travel policies, depending on terms)
- High-risk activities without add-ons (sports/adventure travel)
- Unlicensed driving or illegal activity (auto claims)
- Certain natural disasters without extra coverage (flood/earthquake)
Always read the coverage details, limits, deductibles, and exclusions.
The most common types of personal insurance
Here are the main policy categories most people consider:
1) Health Insurance
Helps cover medical costs such as hospital stays, tests, medications, and sometimes outpatient care. Plans often include limits, waiting periods, networks, and cost-sharing (deductibles/copays).
2) Life Insurance
Provides a payout to your chosen beneficiaries if you pass away. Many people choose term life insurance for affordability, while whole/permanent life adds long-term features like cash value (depending on country and product type).
3) Auto / Motor Insurance
Protects you financially if your vehicle causes damage or is damaged. Many regions require at least third-party liability coverage. Comprehensive coverage may include theft, fire, and own-damage.
4) Homeowners / Renters Insurance
Home insurance can cover the building and/or contents (depending on policy). Renters insurance typically covers your personal belongings and may include liability coverage—useful even if you don’t own property.
5) Travel Insurance
Covers risks while traveling, such as medical emergencies, cancellation, delays, lost baggage, and emergency evacuation. Coverage varies widely, so comparing exclusions is key.
6) Personal Accident & Disability Insurance
Helps with income replacement or lump-sum benefits after covered accidents or disability. Useful if your income depends on your ability to work.
How to choose the right personal insurance (simple checklist)
Use this checklist before buying any policy:
- Start with your biggest risk: health costs, dependents, vehicle liability, or home/property
- Decide what you must protect: income, savings, family needs, assets
- Choose practical limits: based on your lifestyle and potential worst-case cost
- Understand the deductible/excess: higher deductible often means lower premium
- Check exclusions carefully: especially for health and travel
- Confirm who is covered: spouse, children, parents, household members
- Compare policies using the same settings: same limits, add-ons, and deductible
- Ask about claim process: documents required and typical timelines
How claims usually work (high-level)
Most insurers follow a similar claim process:
- Notify the insurer (as soon as possible)
- Submit details and evidence (documents, photos, reports)
- Insurer reviews coverage terms and exclusions
- Assessment/verification (may involve an adjuster or hospital/repair network)
- Claim decision (approved, partially approved, or denied)
Common documents that may be required:
- Policy number and ID documents
- Medical reports and bills (health/travel)
- Police report (theft/accident, if applicable)
- Photos/videos of damage (property/auto)
- Repair estimates/invoices (auto/property)
- Proof of ownership/value (receipts, warranties, bank statements)
Common mistakes to avoid
- Buying the cheapest policy without reading exclusions
- Underinsuring liability (auto/property liability can be expensive)
- Not updating beneficiaries (life insurance)
- Forgetting to declare important details (can lead to claim rejection)
- Not understanding waiting periods (especially health)
- Assuming travel insurance covers everything (it doesn’t)
FAQ
What personal insurance should I get first?
For most people: health insurance first, then life insurance (if you have dependents), then auto and home/renters based on your situation.
Is life insurance needed if I’m single?
Maybe. It’s most important when someone depends on your income, or you have debts that could impact family members.
Do I need renters insurance?
If you rent, renters insurance can be a low-cost way to protect belongings and liability.
Note: Coverage, pricing, and legal requirements vary by country and insurer. Always verify policy details with official documents or a licensed professional.
Life Insurance for Parents: How Much You Need + Best Type to Buy
If you’re a parent, you’re basically running a tiny company: payroll (your income), operations (childcare),…
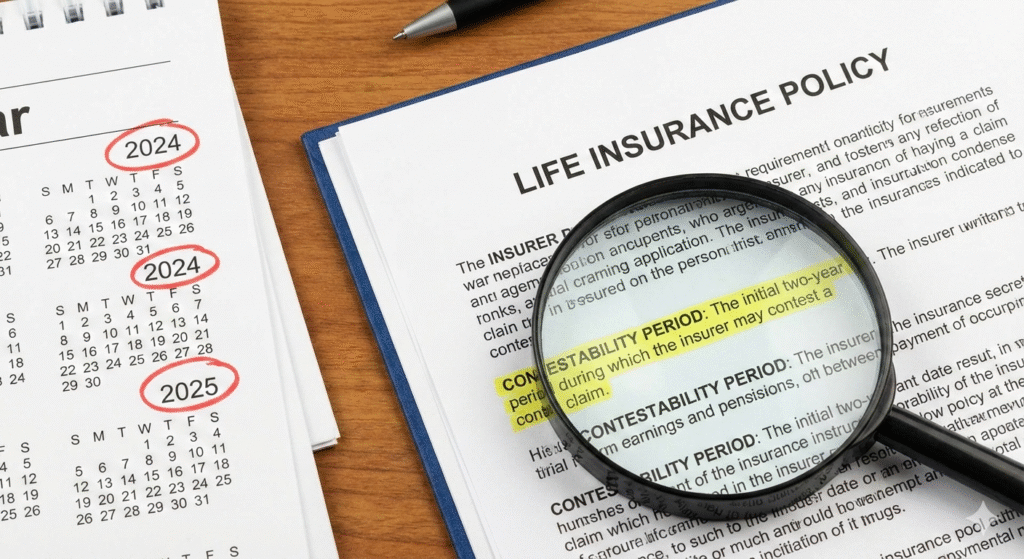
Life Insurance Contestability Period: The 2-Year Rule Explained (2026)
The life insurance contestability period is a time window—often two years from the policy start…
How Long Does It Take to Get Life Insurance Money? Typical Timeline + Delays (2026)
How long does it take to get life insurance money? In many normal cases, beneficiaries…
Does Life Insurance Go Through Probate? When It Does and How to Avoid Delays (2026)
Does life insurance go through probate? Most of the time, no. If a life insurance…
Is Life Insurance Taxable? 9 Situations When You Might Owe Taxes (2026 Guide)
Is life insurance taxable? In most cases, the life insurance death benefit paid to a…
Does Life Insurance Cover Suicide? (2026) Exclusion Period, Claim Rules + What Families Should Do
Does life insurance cover suicide? Yes, in many cases—but many policies include a suicide exclusion…
Multiple Life Insurance Policies (2026): Is It Allowed? Pros, Cons + Smart Layering Strategy
Yes — you can have multiple life insurance policies at the same time. It’s legal,…
Life Insurance Riders Explained (2026): Which Ones Are Worth It + Costs & Traps
When people search for life insurance riders, they usually want one thing: “Which riders are…
Voluntary Life Insurance: What It Is, Cost, Pros & Cons + How It Works (2026)
Voluntary life insurance is optional life insurance you can buy through your employer. Unlike basic…
Supplemental Life Insurance: What It Is, How It Works, Cost + When It’s Worth It (2026)
Supplemental life insurance is exactly what it sounds like: extra life insurance coverage you add…
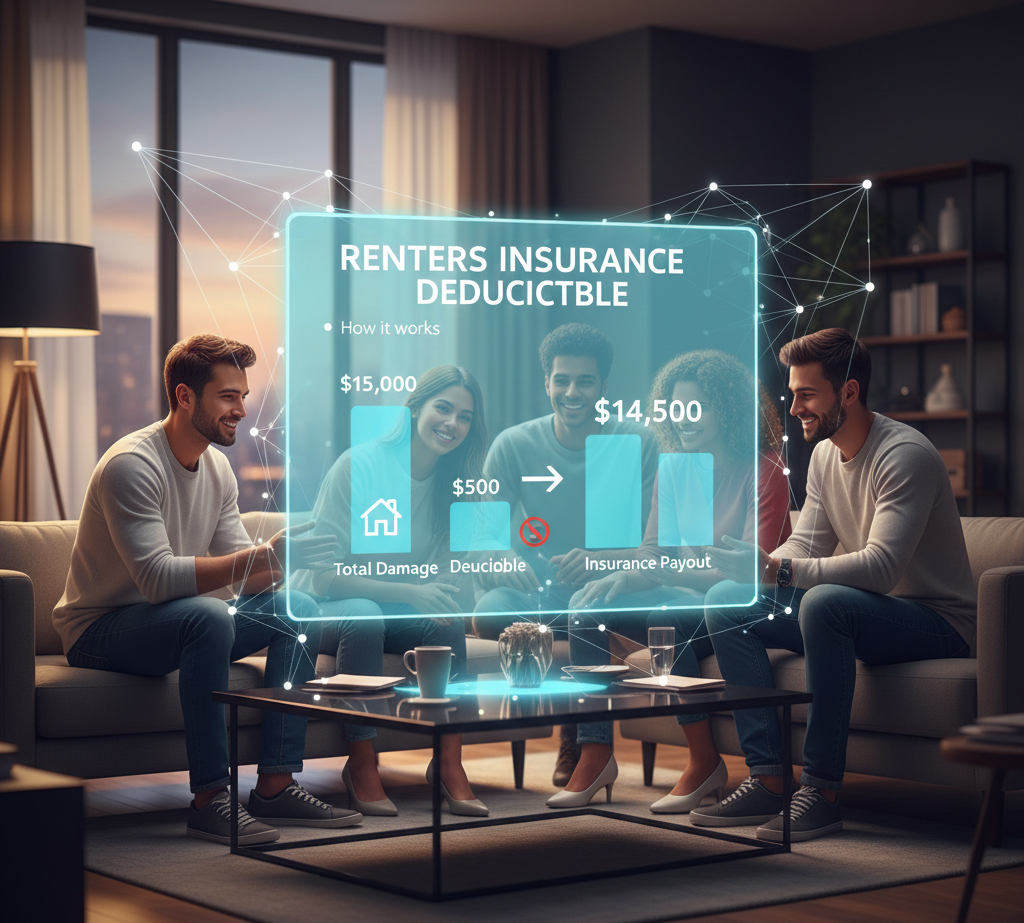
Renters Insurance Deductible Explained: How to Choose the Right Deductible in 2026
A renters insurance deductible is one of the most important parts of your policy—and also…
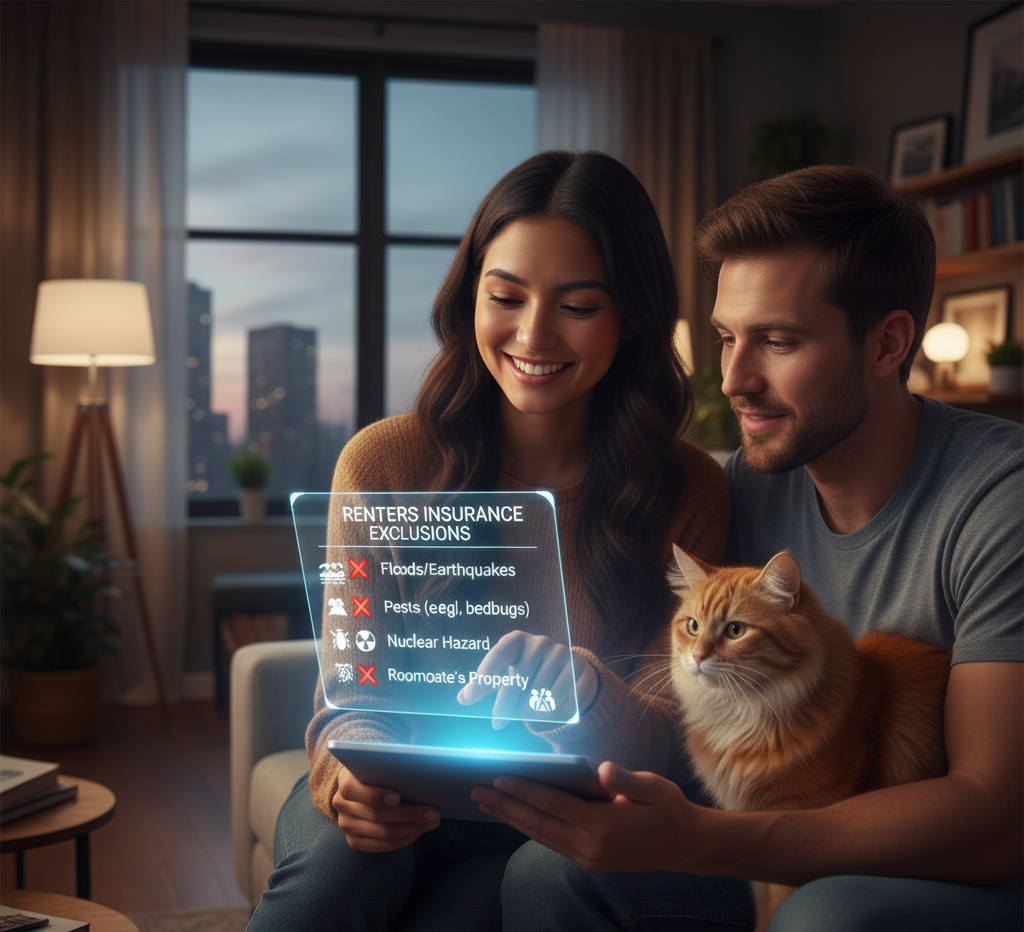
Renters Insurance Exclusions: 9 Things Renters Insurance Usually Doesn’t Cover in 2026 (And How to Fix the Gaps)
Renters insurance exclusions are the #1 reason people feel disappointed after filing a claim. Not…
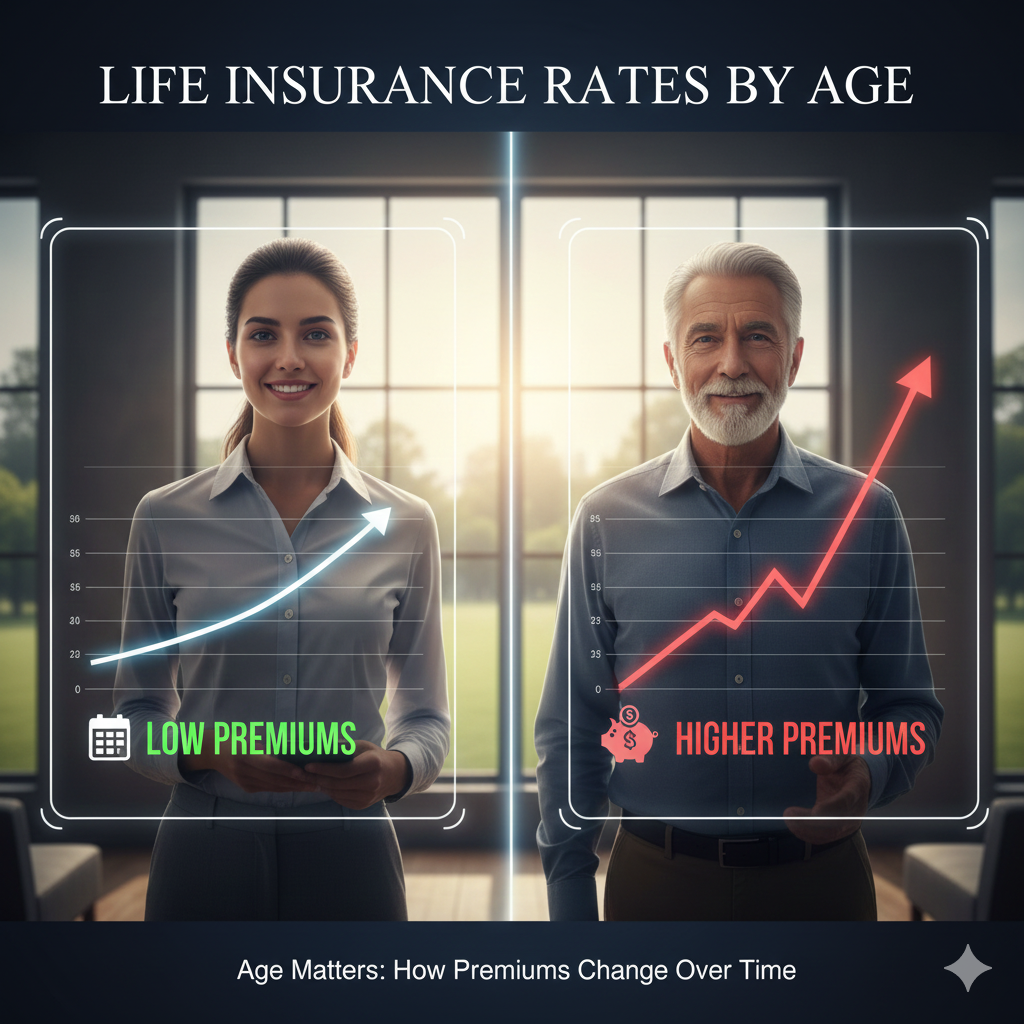
Life Insurance Rates by Age (2026): What Affects Cost + Example Chart
Life insurance rates by age are a big reason people feel “I should have bought…
Life Insurance Beneficiary Rules (2026): How It Works + Common Mistakes
Your life insurance beneficiary is the person (or people) who will receive the insurance payout…
Whole Life Insurance Explained (2026): Cash Value, Pros/Cons + Common Pitfalls)
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance designed to last your entire…
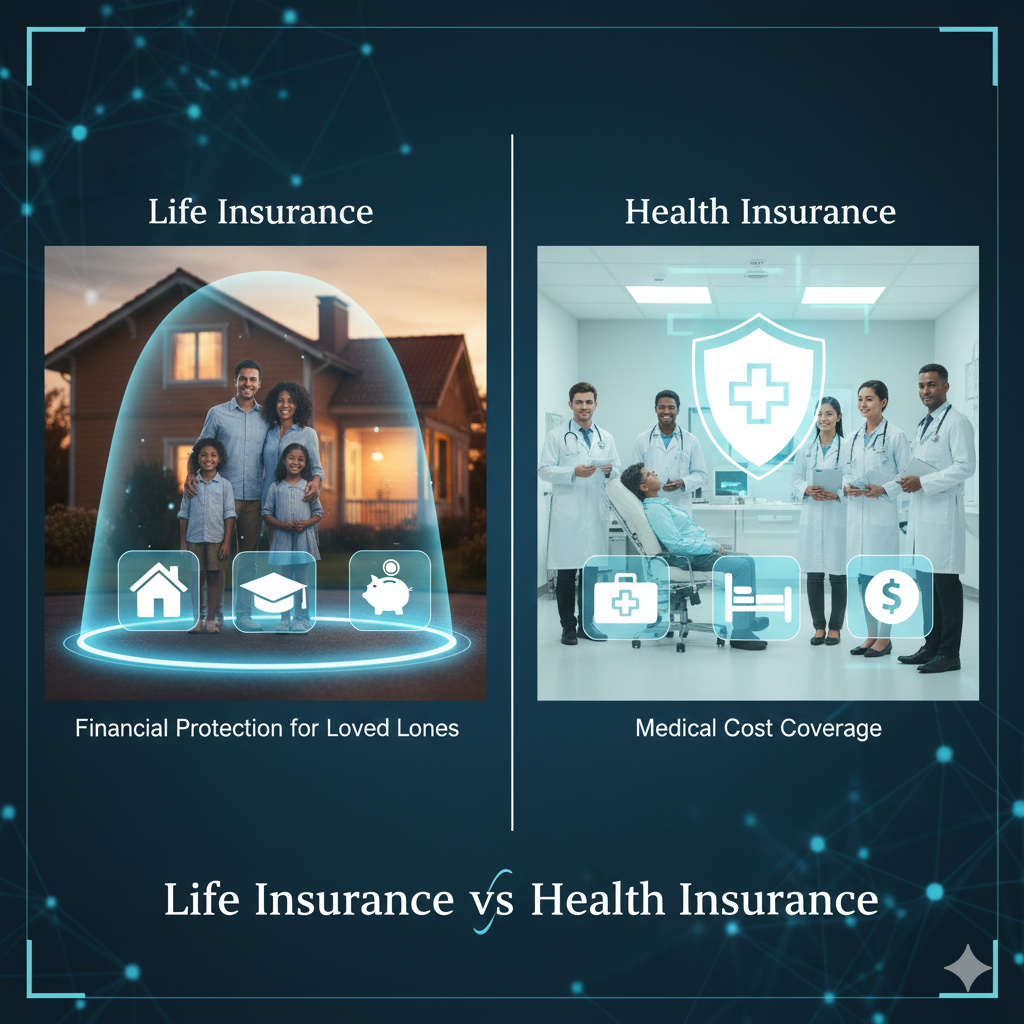
Life Insurance vs Health Insurance: Key Differences + Which One to Buy First
If you’re confused about life insurance vs health insurance, you’re not alone. They sound similar…
Life Insurance for Seniors (2026): Options, Costs + What to Avoid
Life insurance for seniors can still be a smart decision—when it’s bought for the right…
Universal Life Insurance Explained (2026): How It Works, Pros/Cons + Risks
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance designed to provide lifelong coverage…
Group Life Insurance (2026): What Employer Coverage Includes + What’s Missing
Group life insurance is life insurance provided through an employer, organization, or association. Many people…
Life Insurance Exclusions (2026): What’s Not Covered + Common Denial Reasons
Life insurance exclusions are the situations where an insurer may refuse to pay a claim—even…
Life Insurance Claim Process (2026): Steps, Documents + Timeline
The life insurance claim process is what your family goes through to receive the payout…
Term Life Insurance (2026): What It Is, Cost, Pros/Cons + How to Choose
Term life insurance is one of the simplest and most popular ways to protect your…
How Much Life Insurance Do I Need? (Simple Calculator + Examples)
If you’re asking how much life insurance do I need, you’re already doing the smartest…
Term vs Whole Life Insurance: Differences, Pros/Cons + Best Choice
If you’re stuck choosing term vs whole life insurance, you’re not alone. These two types…
Types of Life Insurance Explained (Term, Whole, Universal + More)
Types of life insurance can feel like a menu with way too many options—term, whole,…
Life Insurance Benefits: What It Covers, Advantages + Real Examples
Life insurance benefits are the financial protections your family (or chosen beneficiaries) receive if you…
What is life insurance and why do people buy it?
What is life insurance? It’s a contract where you pay a premium, and the insurer…
SBI Life Insurance: Plans, Benefits, Premium Tips, Riders & Claims (Ultimate 2026 Guide)
TL;DR SBI Life Insurance is best used as a protection-first tool. Start with an SBI…
Max Life Insurance Guide (2026): Plans, Term Cover, Riders, Claims & Checklist
Start with adequate term coverage sized by a simple human-life-value approach. Add riders that protect…
ICICI Prudential Life Insurance (2026): Plans, Benefits, Claim Process & Smart Buying Guide
If you’re researching ICICI Prudential Life Insurance, you’re already doing the most important thing—future-proofing your…
Banner Life Insurance Review (2026): Rates, Riders, and Real Pros & Cons
If you’re shopping term coverage and keep running into Banner Life Insurance, you’re not imagining…
10 Essential Youth Insurance Options: Complete Guide for Financial Security in 2026
Understanding Youth Insurance Options Youth insurance options have become increasingly important as young adults face…
Does Renters Insurance Cover Water Damage from Rain? Complete Guide
When heavy rain hits, renters usually ask one thing: does renters insurance cover water damage…
Right Insurance for Lumolog: Complete Coverage Guide 2026
If Lumolog is on your prescription list, the right insurance Lumolog coverage can be the…
Mycotoxin Testing Insurance Coverage (2026): How to Get Approved + Appeal Denials
Mycotoxin testing insurance coverage is a common question for people dealing with suspected mold exposure…
Single Tooth Implant Cost Without Insurance (2026 Prices + Money-Saving Tips)
Introduction Facing the prospect of a single tooth implant without insurance can be daunting, both…
MyWebInsurance.com Renters MyWebInsurance.com Renters Insurance Review (2026): Coverage, Pros & Cons + Alternatives
Introduction MyWebInsurance.com renters insurance is a renters coverage option many tenants search for when they…